BEVFormer
[ECCV2022] BEVFormer: Learning Bird’s-Eye-View Representation from Multi-Camera Images via Spatiotemporal Transformers
본 논문은 Tesla AI Day 의 핵심 아이디어인 Bird’s-Eye-View로의 변환을 다른 방법으로 구현한다. 미리 정의된 격자 모양의 BEV query를 통해 spatial 및 temporal 정보를 모두 활용하여 vector space로 표현한다.
Abstract
- 미리 정의된 격자 모양의 BEV 쿼리를 통해 공간 및 시간 공간과 상호 작용하여 공간 및 시간 정보를 모두 활용
- spatial information를 집계하기 위해 각 BEV 쿼리가 카메라 뷰 전반에 걸쳐 관심 영역에서 공간 특징을 추출하는 spatial cross-attention를 설계
- temporal information; history BEV information 를 반복적으로 fusion함
1. Introduction
- 라이다 vs. 카메라
- 카메라는 LiDAR 기반 카메라에 비해 장거리 물체를 감지하고 비전 기반 도로 요소(예: 신호등, 정지선)를 식별할 수 있는 이점 존재
- 조감도(BEV): 사물의 위치와 규모를 명확하게 표현하고 지각 및 계획과 같은 다양한 자율 주행 작업에 적합하기 때문에 주변 장면을 일반적으로 사용
- 2D planes → BEV를 생성하는 것은 할 수 없음
- 깊이정보와 3D prior에 의존하지 않고, BEV features를 학습할 수 있는 BEV generating method를 설계하도록 함
- BEV가 시간 및 공간 공간을 연결하는 역할을 수행함
- RNN과 유사하게, 과거에서 현재까지의 시간 정보를 반복적으로 전달
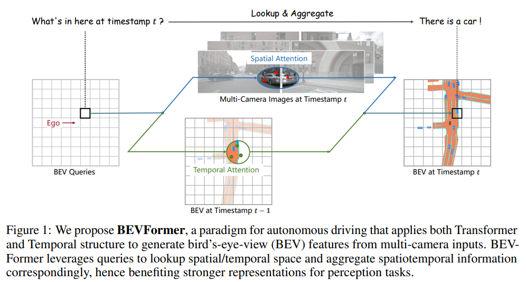
- (1) grid-shaped BEV queries: attention mechanisms으로 → 공간 및 시간 특징을 유연하게 융합
- (2) spatial cross-attention module: multi-camera images에서 spatial features를 aggregate(집계)
(3) temporal self-attention module: history BEV features에서 temporal information을 추출
- contributions
- multi-camera and/or timestamp input → BEV representations에 투영하는 spatiotemporal transformer encoder 인 “BEV Former” 제안
- learnable BEV queries; spatial cross-attention layer and a temporal self-attention layer를 통해 시공간적인 특징 aggregate(집계)
2. Related Work
2-1. Transformer-based 2D perception
- DETR
- cross-attention decoder로 탐지결과를 생성하기 위해 object queries 사용
- 단점: long training time
- Deformable DETR
- 변형가능한 attention
- reference point 근처의 k points만 sampling & attention 결과 보이는 “local regions of interest” 과 상호작용
- ⇒ spatial and temporal information을 효율적으로 집계하기 위해, deformable attention to 3D perception tasks으로 확장함.
2-2. Camera-based 3D Perception
- Previous 3D perception methods; 3D object detection or map segmentation tasks을 독립적으로 수행
- 3D object detection: 2D bounding boxes 기반 → 3D bounding boxes 예측
- DETR3D[47]; 학습 가능한 3D 쿼리를 2D 이미지에 투영 → NMS 후처리 없이 end-to-end 3D bounding box prediction 을 위해 관련 features를 sampling함.
- 깊이정보 사용; 이미지 특징 → BEV 특징으로 변환
- depth estimation [46] or categorical depth distribution [34]
- OFT [36] and ImVoxelNet [37]: 장면의 voxel 표현을 생성하기 위해 미리 정의된 voxel을 이미지 기능에 투영
- 간단한 방법; IPM(Inverse Perspective Mapping)을 통해 투시도를 BEV로 변환
- Lift-Splat[32]; 깊이 분포를 기반으로 BEV 특성을 생성
- proposed spatiotemporal transformer
- 공간적 단서와 시간적 단서를 모두 고려하여 현재 시간의 BEV 특성을 생성
- RNN 방식으로 이전 BEV 특성에서 시간 정보를 얻으므로 계산 비용이 거의 들지 않음.
3. BEVFormer
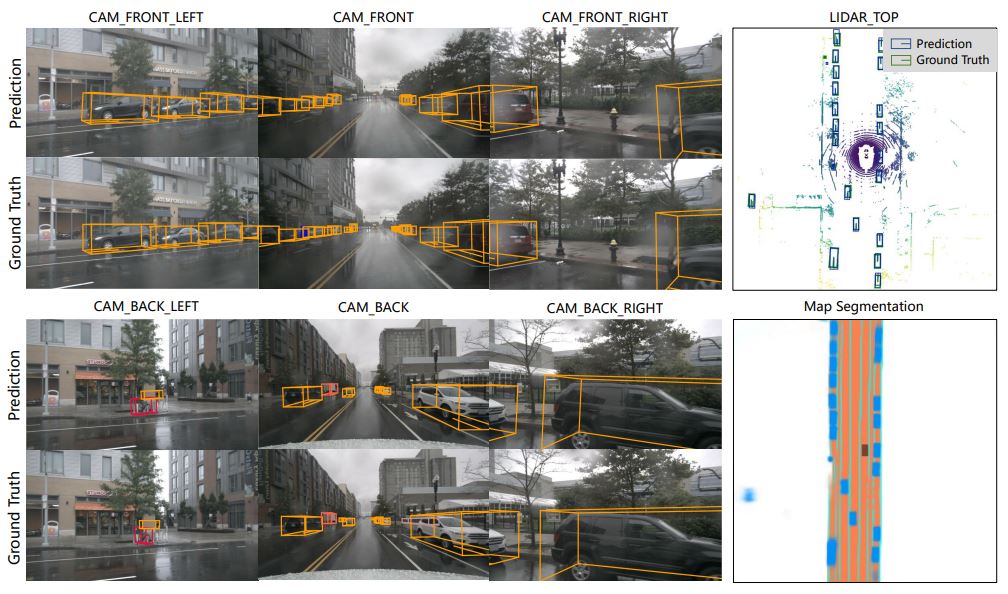
- multi-camera image features → bird’s-eye-view (BEV); 다양한 자율 주행 인식 작업에 대한 통합된 주변 환경 표현을 제공
- multi-view cameras의 spatiotemporal features & attention mechanisms → history BEV features을 효과적으로 aggregate 할 수 있음.
3-1. Overall Architecture
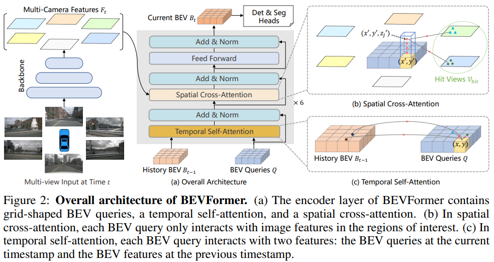
- 6개의 인코더 레이어 - BEV queries, spatial cross attention, and temporal self-attention
- 제외하고는 기존 transformer 구조와 동일
- BEV queries: attention mechanisms을 통해 multi-camera views로부터 BEV 공간의 기능을 쿼리하도록 설계된 격자 모양의 학습 가능한 매개변수
- Spatial cross-attention and temporal self-attention: BEV queries와 함께 작동하는 layer
- BEV 쿼리에 따라 다중 카메라 이미지의 공간적 특징과 과거 BEV의 시간적 특징을 조회하고 집계하는 데 사용
- 과정
- multi-camera images → backbone network(ResNet-101) → features
- 동시에 history BEV features 보존하고 있음.
- each encoder layer에서 temporal self-attention
- 첫번째 사용 시, just self-attention
- Q와 Bt-1을 통해 temporal information 얻음
- Q를 통해 spatial cross-attention
- multi-camera features Ft 에서 spatial information 얻음
- feed-forward network
- refined(정제된) BEV features 출력
- Bt → 3D detection head → 3D bounding boxes and semantic map 예측
3-2. BEV Queries
- BEV query의 각각의 그리드 셀은 실제 세계의 s미터에 해당
- bev feature의 중심은 default로 ego car의 위치에 해당
- bev query에는 학습 가능한 위치 임베딩 추가되어 있음
3-3. Spatial Cross-Attention
- spatial cross-attention based on deformable attention [55]
- Deformable DETR: Deformable Transformers for End-to-End Object Detection (ICLR2021) https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.04159
- 높은 computational cost를 줄이기 위해, 각 BEV 쿼리 Qp가 카메라 뷰 전체에서 관심 영역과만 상호 작용하도록 함.
- but, 원래 deformable attention은 2D 인식을 위해 설계되었음 → 3D 장면에서는 약간의 조정이 필요함[20]
- PointPillarsx: Fast Encoders for Object Detection From Point Clouds https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_CVPR_2019/html/Lang_PointPillars_Fast_Encoders_for_Object_Detection_From_Point_Clouds_CVPR_2019_paper.html
- BEV 평면의 각 쿼리를 기둥과 같은 쿼리로 lift[20]
- pillar에서 Nref 3D reference points 샘플링 → 2d views에 projection
- Vhit; 2D 포인트를 쿼리 Qp의 reference points로 간주하고, 이 reference points 주변의 조회수 Vhit에서 features을 샘플링
- deformable attention의 출력으로 샘플링된 features의 가중치 합을 수행
- 투영 함수 P에서 뷰 이미지의 기준점을 얻는 방법
- Q의 p = (x, y)에 위치한 쿼리 Qp에 해당하는 실제 위치 (x0 , y0) 계산
- ego car의 높이에 따라 (x’,y’,z’)
- 카메라의 투영 행렬을 통해 3D 기준점을 서로 다른 이미지 views에 투영
3-4. Temporal Self-Attention
- 움직이는 물체의 속도를 유추 or 시간적 단서 없이 정지된 이미지에서 심하게 가려진 물체를 감지하는 것을 위함
- same grid correspond to the same real-world location위해, ego-motion에 따라 Bt−1 을 Q에 정렬
offsets ∆p; concatenation of Q and B0 t−1의해 예측
- 이점
- velocity estimation의 acc 향상
- 물체의 위치, 방향 예측의 정확도 향상
- 과거 정보를 포함하기 때문에 → 가려진 객체에 대해 높은 recall을 얻을 수 있음.
해당 포스트는 아래를 참고하여 작성되었습니다.
- [BEVFormer] https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.17270